Diabetes & Pregnancy
During pregnancy the increased glucose level in the blood has a bad effect
on the development of the foetus. Therefore it is important that glucose
level
remains in control throughout pregnancy.
Pregnancy is safe in diabetic patients provided some precautions are
followed.
Before the discovery of insulin pregnancy in diabetes was dangerous for both
mother and foetus.
Most important thing to remember is that no oral drug should be given in a
diabetic pregnant lady. The ideal method of controlling diabetes in a
pregnant
lady is by insulin hormone.
The availability of insulin has made it possible to have a safe pregnancy
outcome.
Two types of Diabetes can occur in pregnancy:
1. Normal female without history of diabetes before
pregnancy:
If a normal female develops diabetes during pregnancy (generally after 24
weeks
of pregnancy), it is known as Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM).
This is more common in females above the age of 30, overweight and those who
have
positive family history of diabetes.
During pregnancy many hormonal changes take place in the body which decrease
the
efficiency of insulin. This increases the requirement of insulin. Females in
whom this extra insulin is not produced go on to have Gestational Diabetes.
This
condition occurs in 3% of the females.
Here it is important to know that Gestational Diabetes is different from
Pre-Gestational Diabetes. If a female who is already diabetic, becomes
pregnant
then such a condition is called Pre-Gestational Diabetes.
Diagnosis of GDM:
Around 24th week of pregnancy blood glucose level in fasting state and one
hour,
two hour, three hour post 75 gm oral glucose is tested. Following table
shows
the upper limit of normal value for blood glucose:
| Time |
Glucose mg/dl |
| Fasting |
95 |
| 1 hr post 75 gm glucose |
180 |
| 2 hr post 75 gm glucose |
140 |
If two of the above four reports are above the normal value the patient is
diagnosed as a case of GDM.
In GDM initially patient is advised to make dietary changes and if glucose
level
does not come down with diet alone then insulin treatment is started.
2. Females with Pre-existing Diabetes and
Pregnancy:
Patients with diabetes willing for pregnancy should consider this option in a
planned manner.
It is important to note that if a diabetic female patient suffers from any of
the following serious disorders, she should not opt for pregnancy.
- Severe heart disease.
- High blood pressure
- Diabetic Retinopathy (Severe NPDR or Proliferative DR)
- Diabetic Nephropathy
Advise before Conception:
- If diabetes is under control by diet and exercise alone then pregnancy
can
be planned. If glucose is on the higher side then it has to be
controlled by
insulin before planning pregnancy.
- If patient is taking oral drugs for diabetes then this has to be
modified
and patient has to be put on insulin. . Insulin treatment is the safest
option in diabetes with pregnancy.
- If patient is on insulin before pregnancy then blood glucose should be
controlled before conception. During pregnancy only Human Insulin should
be
used.
Target glucose level during pregnancy:while on treatment
| Time |
Glucose mg/dl |
| Fasting |
<95 |
| 1 hr post meal |
<140 |
| 2 hr post meal |
<120 |
Precautions during pregnancy:
- Avoid artificial sweeteners.
- Do not consume alcohol.
- Do not smoke.
- Divide daily meals in 6-8 parts.
- Regular Kidney and Eye checkup.
Expectations from Pregnant Diabetic Patients:
- Follow diet instruction sincerely.
- Glucose self monitoring with help of Glucometer.
- Insulin self injection.
- Should be able to identify and manage hypoglycemia.
- maintain food diary (daily / weekly )
Breast Feeding:
- Mother’s milk is most important for the new born. All diabetic mothers
can
breast feed their babies
how to monitor sugars after delivery (those who has normalise
sugars after
delivery )
- sugar monitoring fbs,ppbs after one month of delivery and then check 3
monthly fbs,ppbs,hba1c and than yearly monitoring sugar level.
- GDM resolves after pregnancy in majority of cases.
- recurrent gdm in subsequent pregnancy
- history of gdm were tested for type 2 dm after delivery 40%of time.
General instruction and dietary management in
GDM
(Gestational diabetes mellitus = Diabetes in pregnancy)
it is advise to consult your doctor / gynecologist / dietician for
customization
of dietary changes according to your health / fitness.
High blood sugar levels during pregnancy may be harmful to both the woman and
the
growing fetus. It is important to monitor how many carbohydrates are present
in
the diet — including the type of carbohydrate and the frequency of
consumption —
to help manage blood sugar levels.
Keeping a food diary may make this easier. It is also important for women
with
gestational diabetes to monitor and log their blood sugar levels according
to a
doctor’s directions. Most women will need to check these levels in the
morning
and between meals. The results can indicate the amount and type of food that
is
safe for them to eat.
Monitoring carbohydrates
It can help to space meals and snacks that contain carbohydrates evenly
throughout the day. Doing this can reduce the size of blood sugar spikes
after
eating.
The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development recommend that
women
with gestational diabetes consume at least three small-to-medium meals and
between two and four snacks per day.
Other ways to help regulate blood sugar include:
- refraining from eating too many carbohydrates at one time
- sticking to foods that contain complex carbohydrates, such as fiber
- combining carbohydrates with protein or healthful fats
- avoiding skipping meals
- eating a protein-rich and high fiber breakfast
Eating low glycemic index foods
Eating foods that have a low glycemic index (GI) is another crucial factor
in a
gestational diabetes diet.
GI measures how rapidly a particular food increases blood sugar levels. The
body
breaks down foods with a low GI more slowly than those with a high GI.
The index classifies foods with a score of 55 or below as low GI. These foods
are
ideal for women with gestational diabetes who are trying to manage their
blood
sugar levels.
Low GI foodsTrusted Source to eat include:
nonstarchy vegetables
some starchy vegetables, such as peas and carrots
- some fruit, such as apples, oranges, kiwi, grapefruit, peaches, and
pears
- beans
- lentils
- chickpeas
All of these low GI foods release sugar into the blood slowly, which helps
keep
blood sugar levels stable.
Eating more protein
Eating protein alongside carbohydrates or choosing carbohydrate-rich foods
that
also provide protein helps balance blood sugar levels. Women with
gestational
diabetes should try to eat nutritious, protein-rich foods, such as:
- tofu
- beans : soybean, chickpeas, lentils
- nuts : almond, cashews, pistachios, walnuts
- seeds : hempseed, chia seed, flex seed, pumpkin seed
- qunioa
- legumes
- soya milk
- oats
- peanut butter
- fish, chicken, turky
- eggs
Choosing unsaturated fats
Unsaturated fats are also part of any healthful diet.
- Go easy on butter, margarine, salad dressing, cooking oil, and desserts.
- Avoid fats high in saturated fat such as hamburger, cheese, bacon, and
butter.
- Don't cut fats and oils from your diet entirely. They provide energy for
growth and are essential for baby's brain development.
- Choose healthy oils, such as canola oil, olive oil, peanut oil, and
safflower oil. Include nuts, avocados, and olives.
Foods to avoid
Avoiding foods that may excessively raise blood sugar levels is essential if
a
person is following a gestational diabetes diet.
Avoiding sugary foods
Blood sugar levels increase when people eat sugary foods, particularly those
that
have undergone refinement or processing. Women with gestational diabetes
should
avoid or limit sugary foods as much as possible.
Sugary foods to avoid include the following:
- cakes
- cookies
- candy
- desserts
- sweet pastries
- soda
- ice cream
- fruit juice with added sugar
Women with gestational diabetes can enjoy milk and fruits in moderation, even
though they contain natural sugars.
Avoiding highly starchy foods
Starchy foods are high in carbohydrates and can have a significant effect on
blood sugar, so it is important to eat them only in small portions. It is
best
to avoid or limit very starchy foods, including:
- white potatoes
- white bread
- white rice
- white pasta
Although whole grains, such as whole wheat pasta and brown rice, are more
nutritious, they are still high in carbohydrates. As a result, these foods
may
also be best in moderation.
Avoiding hidden sugars and carbohydrates
as consuming more salt can lead to water retention and further increase
swelling
during pregnancy and can also lead to gestational hypertension, which along
with
gestational diabetes can be very risky for both the mother and the baby
Avoiding highly starchy foods
Some foods and drinks are not obviously sources of sugar or carbohydrates.
However, they may still contain potentially harmful levels of both. Examples
of
these products include:
- highly processed foods
- some condiments, such as dressings and ketchup
- fast foods
- alcohol
MEDICAL NUTRITION THERAPY IN GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS
Women with GDM should be counselled by a dietitian once the diagnosis is made
to
initiate MNT which is the mainstay of any
management plan. The aim is to attain normal glycemic control without
ketosis
and fetal compromise along with adequate weight
gain based on prenatal BMI. MNT should allow sufficient calories for the
mother
and the developing fetus while avoiding excess
weight gain and prandial hyperglycemia. The calorie requirement depends on
factors such as pre-pregnancy weight, stage of
pregnancy, activity levels and blood glucose levels. No incremental calorie
intake is recommended during the first trimester.
approximately 350 kcal/day additional (only in the second and third
trimester)
is regarded as adequate.
Pre-pregnancy body mass index-adjustment calorie requirement during
pregnancy
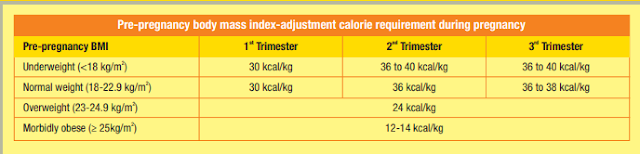
Calorie intake may be reduced (if overweight/obese), but should not be below
1600-1800 kcal/day Monitoring weight changes is important to ensure the
adequacy
of MNT and to gain weight within the recommended limits. It is very
important to
avoid skipping meals. This is because nutritional needs are increased for
optimal growth and development of the foetus.
Ways to reduce post-meal glucose spikes
1. MNT comprising of three meals and mid-meal snacks (low in
carbohydrates and moderate amounts of protein at regular intervals is
recommended to allow even distribution of carbohydrates throughout the day.
A minimum of
175 g/day carbohydrates should be ensured.
2. including fibre aids in improving safety, prevents constipation and
helps in stabilizing blood glucose levels. The recommended fibre intake for
women is 25-40 g/day. Consumption of adequate fibre in the form of whole
grains, millets, legumes and whole fruits and vegetables should be advised.
3. Carbohydrates are generally not as well tolerated at breakfast as in
other meals. This is because during pregnancy in most cases dawn phenomenon
appears to contribute to morning glucose intolerance. Hence, it is advised
to split the breakfast in to two parts with a 2hr gap.
સગર્ભાવસ્થામાં ડાયાબિટીસ (જીડીએમ) માં મહત્વની સૂચના
અને
ખોરાક અંગેની માહિતી
GDM - DIABETES IN PREGNANCY / GESTATIONAL DIABETES ) = સગર્ભાવસ્થામાં
ડાયાબિટીસ
સગર્ભાવસ્થા દરમિયાન ડાયાબિટીસમા તમારા સ્વાસ્થ્ય / તંદુરસ્તી અનુસાર આહાર
ફેરફારોને
કસ્ટમાઇઝ કરવા માટે તમારા ડોક્ટર /ગાયનેકોલોજિસ્ટ / ડાયેટિશિયનની મુલાકાત
લેવાની
સલાહ છે.
સગર્ભાવસ્થા દરમિયાન બ્લડ સુગરનું ઉચ્ચ સ્તર, તે સ્ત્રી અને વધતા જતા ગર્ભ બંને
માટે
નુકસાનકારક થાઈ શકે છે.
કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટનો પ્રકાર અને વપરાશની આવર્તન સહિત - આહારમાં કેટલા
કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટ્સ
હાજર છે તે લોહીમાં ડાયાબિટીસના સ્તરને સંચાલિત કરે છે એટલે તેનું નિરીક્ષણ
કરવું
મહત્વપૂર્ણ છે.
ફૂડ ડાયરી રાખવી એ આને સરળ બનાવી શકે છે. સગર્ભાવસ્થાના ડાયાબિટીસવાળા મહિલાઓ
માટે
પણ ડોક્ટરની સૂચનાઓ અનુસાર તેમના બ્લડ સુગરના સ્તરોનું નિરીક્ષણ અને તેનું
નિયમિત
નોંધ કરવું મહત્વપૂર્ણ છે. મોટાભાગની સ્ત્રીઓને સવારે અને ભોજનની વચ્ચે આ સ્તરો
તપાસવાની જરૂર રહે છે. આ તાપસના પરિણામો એટલે કે બ્લડ સુગર ખાવા માટે સલામત
ખોરાકનો
જથ્થો અને પ્રકાર સૂચવે છે.
કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનું નિરીક્ષણ
કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનું નિરીક્ષણ ભોજન અને નાસ્તા નું પ્રમાણ નક્કી કરવામાં મદદ કરી
શકે
છે જેમાં સમગ્ર દિવસમાં સમાનરૂપે કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટ હોય છે. આ કરવાથી ખાધા પછી
બ્લડ
સુગર સ્પાઇક્સ/ એકદમ વધવું એ ઓછું થઈ શકે છે.
નેશનલ ઇન્સ્ટિટ્યૂટ ચાઇલ્ડ હેલ્થ એન્ડ હ્યુમન ડેવલપમેન્ટ ભલામણ કરે છે કે
સગર્ભાવસ્થાના ડાયાબિટીસવાળા મહિલાઓ દરરોજ ઓછામાં ઓછા ત્રણ નાના-મધ્યમ ભોજન અને
બે
થી ચાર વાર નાસ્તો લેવો જોઈએ.
બ્લડ સુગરને નિયંત્રિત કરવામાં મદદ કરવાની અન્ય રીતોમાં આ
શામેલ
છે
- એક સમયે ઘણા બધા કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટ ખાવાથી દૂર રહેવું.
- ફાઇબર જેવા જટિલ કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટ ધરાવતા ખોરાકને વળગી રહેવું.
- પ્રોટીન અથવા આરોગ્યપ્રદ ચરબી સાથે કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનું સંયોજન.
- ભોજન છોડવાનું ટાળવું.
- પ્રોટીનથી સમૃદ્ધ અને ઉચ્ચ ફાઇબર નાસ્તો ખાવું.
ઓછી ગ્લાયકેમિક ઇન્ડેક્સ વાળા ખોરાક લેવા
સગર્ભાવસ્થાના ડાયાબિટીસના આહારમાં નિમ્ન ગ્લાયકેમિક ઇન્ડેક્સ (જીઆઈ) હોય તેવા
ખોરાક ખાવું એ બીજું નિર્ણાયક પરિબળ છે.
કોઈ ચોક્કસ ખોરાક લેવાથી લોહીમાં શર્કરાના સ્તરમાં કેટલી ઝડપથી વધારો થાય છે એને
ગ્લાયકેમિક ઇન્ડેક્સ કહેવાય છે. શરીર વધુ જીઆઈવાળા કરતા ઓછી જીઆઈવાળા ખોરાકને
ધીમે
ધીમે તોડી નાખે છે.
સૂચકાંક ખોરાકને 55 અથવા તેથી નીચેના GI વાળા એમ નીચેના વર્ગમાં વર્ગીકૃત કરે
છે. આ
ખોરાક સગર્ભાવસ્થા ડાયાબિટીસવાળી સ્ત્રીઓ માટે આદર્શ છે જેઓ તેમના બ્લડ સુગરના
સ્તરનું સંચાલન કરવાનો પ્રયાસ કરી રહ્યા છે.
ઓછા ગ્લાયકેમિક ઇન્ડેક્સ વાળા આહારના પ્રમાણિત સ્રોતમાં નીચેના મુજબનો
આહાર
ખાવા માટે શામેલ થાઈ છે:
સ્ટાર્ચ વગરના શાકભાજી
કેટલીક સ્ટાર્ચ વાળા શાકભાજી જેમ કે
- વટાણા અને ગાજર
- સફરજન, નારંગી, કીવી, ગ્રેપફ્રૂટ, પીચ અને નાશપતીનો જેવા કેટલાક ફળ
- કઠોળ
- દાળ
- ચણા
આ બધા ઓછા જીઆઈ વાળા ખોરાક ધીમે ધીમે લોહીમાં ખાંડ છોડે છે, જે બ્લડ સુગરના સ્તર
સ્થિર રાખવામાં મદદ છે.
વધુ પ્રોટીન ખાવું
કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટની સાથે પ્રોટીન ખાવાનું અથવા કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટયુક્ત ખોરાક કે જે
પ્રોટીન પણ પૂરો પાડે છે તે પસંદ કરવાથી લોહીમાં બ્લડ સુગરના સ્તરને સંતુલિત
કરવામાં મદદ મળે છે. સગર્ભાવસ્થા ડાયાબિટીઝની સ્ત્રીઓએ પોષક, પ્રોટીનયુક્ત
ખોરાક
ખાવાનો પ્રયત્ન કરવો જોઈએ, જેમ કે:
- ટોફુ
- કઠોળ: સોયાબીન, ચણા, દાળ
- નૂટસ: બદામ, કાજુ, પિસ્તા, અખરોટ
- બીજ: હેમ્પ્સીડ, ચિયા બીજ, ફ્લેક્સ સીડ, કોળાના બીજ
- ક્વિનોઆ
- કઠોળ
- સોયા દૂધ
- ઓટ્સ
- મગફળીનું માખણ
- માછલી, ચિકન અને ટર્કી
- ઇંડા
અસંતૃપ્ત (Unsaturated fat ) ચરબીવાળા ખોરાક પસંદ કરવા
અસંતૃપ્ત ચરબી એ પણ આરોગ્યપ્રદ આહારનો એક ભાગ છે.
- માખણ, માર્જરિન, કચુંબર ડ્રેસિંગ, રસોઈ તેલ અને મીઠાઈઓ ઓછા લેવા.
- સંતૃપ્ત ચરબીવાળા ખોરાકને ટાળો જેમ કે હેમબર્ગર, ચીઝ, બેકન અને માખણ.
- તમારા આહારમાંથી ચરબી અને તેલને સંપૂર્ણપણે કાપશો નહીં કારણ કે બાળકના
મગજના
વિકાસ માટે જરૂરી શક્તિ પ્રદાન કરે છે.
- કેનોલા તેલ, ઓલિવ તેલ, મગફળીના તેલ અને કેસર તેલ જેવા સ્વસ્થ તેલ પસંદ કરો.
બદામ, એવોકાડો અને ઓલિવ શામેલ કરો.
આ ખોરાક ટાળો:
જો કોઈ વ્યક્તિને સગર્ભાવસ્થામાં ડાયાબિટીસ હોઈ તો લોહીમાં બ્લડ સુગરના સ્તરને
વધારે
પ્રમાણમાં વધારી શકે તેવા ખોરાકને ટાળવો જરૂરી છે.
સુગરયુક્ત ખોરાક ટાળો
જ્યારે લોકો સુગરયુક્ત ખોરાક ખાય છે, ખાસ કરીને જેમાં શુદ્ધિકરણ અથવા પ્રક્રિયા
કરી
છે તે બ્લડ સુગરનું પ્રમાણ વધારે છે.
સગર્ભાવસ્થા ડાયાબિટીસવાળા સ્ત્રીઓને શક્ય તેટલું સુગરયુક્ત ખોરાકને ટાળવું
અથવા
મર્યાદિત કરવું જોઈએ.
સુગર આધારે એવા ખોરાકમાં નીચેનાનો સમાવેશ થાય છે જે ટાળવા
જોઈએ:
- કેક
- કૂકીઝ
- કેન્ડી
- મીઠાઈઓ
- મીઠી પેસ્ટ્રીઝ
- સોડા
- આઈસ્ક્રીમ
- ફળનો રસ જેમાં ખાંડ ઉમેરેલ હોઈ.
સગર્ભાવસ્થામાં ડાયાબિટીઝની મહિલાઓ દૂધ અને ફળોનો મધ્યસ્થતામાં આનંદ લઈ શકે છે,
ભલે
તેમાં કુદરતી શર્કરા હોય.
ખૂબ સ્ટાર્ચયુક્ત ખોરાક લેવાનું ટાળો
સ્ટાર્ચયુક્ત ખોરાકમાં કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનું પ્રમાણ વધુ હોય છે અને તે બ્લડ સુગર પર
નોંધપાત્ર અસર કરી શકે છે, તેથી ફક્ત તેને નાના ભાગોમાં જ ખાવું મહત્વપૂર્ણ છે.
ખૂબ
સ્ટાર્ચયુક્ત ખોરાકને ટાળવું અથવા મર્યાદિત કરવું શ્રેષ્ઠ છે, જેવા કે:
- સફેદ બટાટા
- સફેદ બ્રેડ
- સફેદ ભાત
- સફેદ પાસ્તા
તેમ છતાં આખા અનાજ, જેમ કે આખા ઘઉંના પાસ્તા અને ભૂરા ચોખા, વધુ પોષક છે, તેમ
છતાં
તે કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટની માત્રામાં વધારો કરે છે. પરિણામે, આ ખોરાક મધ્યસ્થતામાં પણ
શ્રેષ્ઠ હોઈ શકે છે.
મધ્યસ્થતામાં મીઠું રાખો
કારણ કે વધુ મીઠું લેવાથી પાણીની રીટેન્શન થઈ શકે છે અને ગર્ભાવસ્થા દરમિયાન
સોજો
વધે છે અને સગર્ભાવસ્થાના હાયપરટેન્શન પણ થઈ શકે છે, જે સગર્ભાવસ્થા
ડાયાબિટીસની
સાથે માતા અને બાળક બંને માટે ખૂબ જોખમી બની શકે છે.
છુપાયેલ શર્કરા અને કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટ્સ ટાળવું:
કેટલાક ખાદ્યપદાર્થો અને પીણાં ખાંડ અથવા કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનાં સ્રોત નથી. જો કે,
તેમાં
હજી પણ બંનેના સંભવિત હાનિકારક સ્તર હોઈ શકે છે. આ ઉત્પાદનોના ઉદાહરણોમાં શામેલ
છે:
- ખૂબ પ્રોસેસ્ડ ખોરાક
- કેટલાક મસાલા, જેમ કે ડ્રેસિંગ્સ અને કેચઅપ
- ફાસ્ટ ફૂડ
- આલ્કોહોલ
મેડિકલ ન્યુટ્રિશન થેરાપી ઇન જેસ્ટિશનલ ડાયાબિટીસ મેલાઇટીસ
એકવાર જી.ડી.એમ. ધરાવતી મહિલાઓએ ડાયેટિશિયન દ્વારા સલાહ લેવી જોઈએ કે એકવાર
નિદાન
થયા પછી એમ.એન.ટી. જે કોઈ પણનો મુખ્ય આધાર છે.
ઉદ્દેશ્ય એ છે કે કીટોસિસ અને ગર્ભના સમાધાન વિના સામાન્ય ગ્લાયસેમિક નિયંત્રણ
પ્રાપ્ત કરવું, તેમજ પૂરતા વજન સાથે
પ્રિનેટલ BMI ના આધારે ગેઇન. MNT એ માતા અને વિકાસશીલ ગર્ભ માટે પૂરતી કેલરીની
મંજૂરી આપવી જોઈએ જ્યારે વધુને ટાળો
વજનમાં વધારો અને રોગનિવારક હાયપરગ્લાયકેમિઆ. કેલરી આવશ્યકતા ગર્ભાવસ્થાના
પૂર્વ
વજન, તબક્કા જેવા પરિબળો પર આધારિત છે
ગર્ભાવસ્થા, પ્રવૃત્તિના સ્તરો અને લોહીમાં સુગરનું સ્તર. પ્રથમ ત્રિમાસિક
દરમ્યાન
કોઈ વધારાની કેલરી લેવાની ભલામણ કરવામાં આવતી નથી.
આશરે 350 કેલેરી/દિવસનો વધારાનો (ફક્ત બીજા અને ત્રીજા ત્રિમાસિકમાં) પૂરતો
ગણવામાં
આવે છે.
ગર્ભાવસ્થા દરમિયાન પૂર્વ-ગર્ભાવસ્થા બોડી માસ ઇન્ડેક્સ-એડજસ્ટમેન્ટ કેલરી
આવશ્યકતા
કેલરીનું સેવન ઓછું થઈ શકે છે (જો વધારે વજન / મેદસ્વી હોય તો), પરંતુ 1600-1800
કેલેરી / દિવસથી નીચે ન હોવું જોઈએ એમએનટીની પર્યાપ્તતાને સુનિશ્ચિત કરવા અને
સૂચવેલ મર્યાદામાં વજન વધારવા માટે વજનના ફેરફારોનું નિરીક્ષણ કરવું મહત્વપૂર્ણ
છે.
ભોજન છોડવાનું ટાળવું ખૂબ જ મહત્વપૂર્ણ છે. આ એટલા માટે છે કારણ કે ગર્ભના
શ્રેષ્ઠ
વિકાસ અને વિકાસ માટે પોષક જરૂરિયાતોમાં વધારો થાય છે.
ભોજન પછી તરત વધતા સુગરને ઘટાડવાની રીતો
1. એમ.એન.ટી. માં ત્રણ ભોજન અને મિડ-ભોજન નાસ્તાનો સમાવેશ થાય છે (નિયમિત
અંતરાલમાં કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટ ઓછું હોય છે અને મધ્યમ માત્રામાં પ્રોટીન હોય છે,
જેથી દિવસ દરમિયાન કાર્બોહાઈડ્રેટનું વિતરણ પણ કરવામાં આવે. ઓછામાં ઓછી 175
ગ્રામ / દિવસ કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટની ખાતરી કરવી જોઈએ.
2. સલામતીમાં સુધારો કરવામાં ફાઇબર ઉમેરા જે, કબજિયાત અટકાવે છે અને
લોહીમાં
શર્કરાના સ્તરને સ્થિર કરવામાં મદદ કરે છે. સ્ત્રીઓ માટે આગ્રહણીય રેસાની
માત્રા 25-40 ગ્રામ / દિવસ છે. આખા અનાજ, બાજરી, લીલીભાજીઓ અને આખા ફળો અને
શાકભાજીના રૂપમાં પર્યાપ્ત રેસાના વપરાશની સલાહ આપવી જોઈએ.
3. કાર્બોહાઇડ્રેટ સામાન્ય રીતે નાસ્તામાં અન્ય ભોજનની જેમ લેવામાં આવતું
નથી.
આ એટલા માટે છે કારણ કે મોટાભાગના કિસ્સાઓમાં ગર્ભાવસ્થા દરમિયાન
ફીનોમેનોનની
ઘટના સવારે ગ્લુકોઝ અસહિષ્ણુતામાં ફાળો આપે છે. આથી, નાસ્તાને એ સાથે બે
ભાગમાં
વહેંચવાની સલાહ આપવામાં આવે છે 2 કલાકના અંતરે.